LDNWebPerf Talk Notes
Introducing A-Frame
The goal of this talk is to introduce the audience to making Virtual Reality for the web using A-Frame components to build A-Frame scenes.
Talk Resources
https://metaverse.samsunginter.net 🡸 Shared VR slide deck!!
https://metaverse.samsunginter.net?watcher 🡸 Just content no participants
https://github.com/adaroseedwards/metaverse 🡸 Source Code
Simple A-Frame scene you can edit: https://jsbin.com/fugatar/edit?html,output
Further Reading
Component - A-Frame
_A web framework for building virtual reality experiences. Make WebVR with HTML and the Entity-Component ecosystem…_aframe.io
Day 4: A Christmas Carol for the Web Future
_We currently stand on the eve of a new era of the web. Virtual Reality in the Web Platform now allows us to bring…_12devsofxmas.co.uk
Realities of doing VR on the Web - The dot Post
_Virtual reality has come to the web! There are now browsers which work inside Virtual Reality headsets. Ada explores…_www.thedotpost.com
Talk Notes
VR is here.
This year at CES VR and AR is one of the biggest areas of excitement.
More and more VR headsets reach the market each year.
VR today is like the Mobile in 2007, it’s in it’s infancy UI patterns and hardware are starting to mature and control patterns are forming.
Like all new platforms there are Web Browsers for VR
Samsung Internet for GearVR
With new platforms there are new APIs for doing enahnce the WebGL to embrace the capabilities of VR.
Right now though it’s based entirely around WebGL which kind of feels divorced from the web.
Who here has written software for GL before?
Who here has done HTML?!
Wouldn’t it be really cool if one could describe scenes like we describe documents using some kind of markup language?!
Fortunately some folks at Mozilla also thought it would be really cool and we have A-Frame.
A-Frame uses the custom elements API to couple custom HTML elements with objects in 3D space.
You can attach pieces of logic known as components to these elements as if they were html attributes.

Child nodes are inherit the transforms of the parent. SO in the example above the child node is placed in the same place as the parent.
Everything is extensible so you can include community components to be able to build complex scenes and interactions without writing a line of JavaScript.
For example: https://jsbin.com/fugatar/edit?html,output
A-Frame looks and writes just like HTML so I am going to introduce how one can work with A-Frame to build cool stuff.
Each of you should have a Google Cardboard, the kind folks at Google gave us 100.
Here is a url for something I made in A-Frame i’m going to describe how I made it.
Getting Started With AFrame
Lets set the scene…
<a-scene></a-scene>
This creates a canvas and any a-frame entities it contains get rendered to that canvas.
Has some default entities which get overriden if added to the scene manually.
- A camera at
position="0 0 0"for rendering the scene. - A directional light
- An ambient light
This allows one to start building a scene without any hassle.
http://metaverse.samsunginter.net/
Adding a 3D object
<a-entity><a-entity>
This acts like a reference in 3D space we can put some content onto using components.
Components are discreet bits of logic written in JavaScript we can reuse.
We can use the geometry component to add a shape to render.
Components are configured by setting HTML attributes.
<a-entity geometry=”primitive: cube;”></a-entity>
There are pre-configured entities known as primitives. For example:
<a-box></a-box>
These can be useful when a complex component wants to provide a default configuration.
Attaching Objects Together
In HTML elements according to their parent.
It is the same in A-Frame too.
You can apply transforms such as scale, position and rotation. to the parent and these get applied to the child as well.
For example here this box has two children, and in rotating the parent the children get rotated too with their relative positions preserved.
In this example I am applying many transforms at different levels of the heirarchy. This allows me to swing the arms and keep the hands attached.
To scale the body and keep everything together.
Configuring the Material
‘Demo on Bunny’
By far the most complex component in terms of flexibility and number of configurable parameters. I won’t touch on everything but here are some useful bits.
material - A-Frame
_A web framework for building virtual reality experiences. Make WebVR with HTML and the Entity-Component ecosystem…_aframe.io
material="color: blue;- Setting the color of the material
material="src: url(/images/texture.png;)" — Setting the image of a material.
You probably want to preload some assets you need quick access to. For this the <a-assets> tag comes in handy.
A-assets blocks scene render until everything is loaded so you can ensure you have the minimum resources to render the scene.
Fill this with <img> <audio> <video> <a-asset-item>

Example a-assets
If you are building a larger scene perhaps be wary of preloading everything. Doing that will make the user wait longer before loading the scene and they may get bored and close the tab.
After all users still as impatient as ever.
The Sky
One of the primitives which can be used to great effect is the sky sphere. <a-sky>
This allows you to set an equirectangular image or video to the sky sphere.
The image format for the Sky is known as an Equirectangular image.
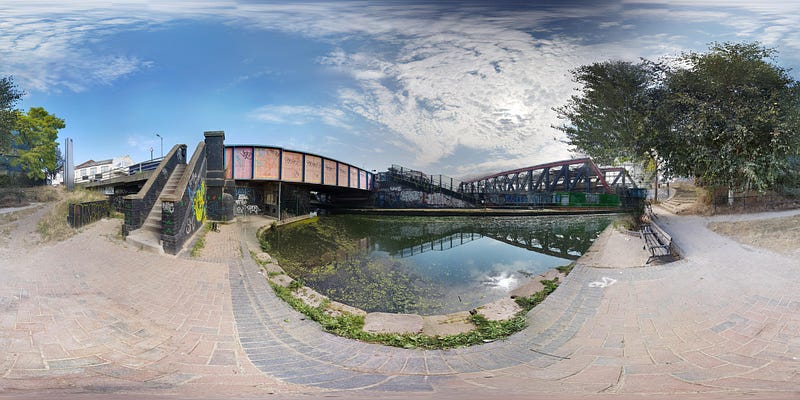

You can generate an equirectangular image from an A-Frame scene by pressing ctrl-alt-shift-s

Making Text
Text is difficult in 3D and some issues in VR.
There are two ways of doing text:
- 3D modeled text
- Bitmap text rendered as a texture.
Both of these can be proceduraly generated on the fly and have a-frame components to use them.
3D Modelled text
Each character is a 3D model
- Visually stunning.
- Each character can take many polygons to render, potentially making the experience slow.
- Use when you only need to render a few characters.
Texture text
This is where the graphics card renders a bitmap image of text to a plane.
- Efficient to render many characters
- Legible up close
- Takes up large amounts of texture memory, due to the mips.
- Small character sets, not suitable for non-latin characters.
- A unicode font could take Gigabytes of Memory!!
Remember that right now everyone in VR has poor eyesight, even the best VR headsets couldn’t pass an eye exam for driving a car.
Show don’t tell
Making 3D models
The built in importers allow you to include 3D models.
<a-entity obj-model="obj: url(model.obj); mtl: url(model.mtl)"></a-entity>
You can optionally only include the model and handle the texture yourself
<a-entity obj-model="obj: #myModel;" material="color: blue;"></a-entity>
How do I make them?
- Maya (My fave, can’t afford)
- Blender (Feature complete, pain in the arse)
- Clara.io (Not many features, simple and a web app, good enough)
- Buy them? Turbo squid.
Physics
This is something which adds a bit of flashiness to any scene. There is a wonderful physics component.
donmccurdy/aframe-physics-system
_aframe-physics-system - Physics system for A-Frame VR, built on CANNON.js._github.com
JSBin to play with it: https://jsbin.com/pawace/edit?html,js,output
Keep physics simple, too much and it won’t work well on mobile.
<!-- a-scene with physics component –>
<!-- camera with a sphere around it to push objects –>
<!-- pushable blue ball –>
<!-- floor to stop objects falling forever –>
</a-scene>
Using JavaScript
There is a wonderful elegance to the way A-Frame is designed. Because it is based on custom html elements you can control it with JavaScript much like you would ordinary html.
Edit the HTML to set some initial state. E.g. lets throw a ball.
var ball = document.querySelector('#myBall');
ball.setAttribute('velocity', '0 5 10');
Elements use events for communication:
ball.addEventListener('collide', function (e) { /* Do something */ });
User interactivity
The in-built cursor component attaches a cursor to the camera which can be used to click on objects.
When someone taps on the screen it works out what the user is looking at and and fires a click event on that object.
This can be used for running some JavaScript.
button.addEventListener('click', function (e) { /* Do something */ });
A case study
This talk was built with A-Frame.
I use websockets to sync the avatars between clients. Each frame I send camera data to the server and all the avatar position data to the websites.
Using javascript .innerHTML I create new avatars, I sync the position and rotation data using .setAttribute on the avatars.
For the dynamic content I just inject a-frame elements using .innerHTML nothing weird or high tech just writing HTML with JavaScript the old fashioned way.
Changing topic a little
Break for Questions (There is more after the questions)
I will update this with the questions asked.
Conclusion (Keep Going)
A-Frame is a library that allows you to work with the 3D scenes in a way which is familiar to any who have worked with HTML.
The goals and problems of WebVR are much the same with developing for the web.
- Users have ever shortening attention spans.
- Networks are still getting more congested.
- Sites are getting larger
It also shares some of the same solutions too.
Preloading
Showing anything fast is far more valuable than showing something complete. Progressive rendering is a cornerstone of the web after all.
a-assets allows you to block rendering on Assets so that you can gain fast access to anything which is required.
But preloading is not something you should do to every asset because if you prioritise everything you prioritise nothing.
One tip I saw was to only preload a low resolution blurred skybox. This gets the user immersed quickly. Then start pulling in the content you need to display after you have started rendering.
If you have spent anytime optimising the performance of your web app then this should be familiar to you.
Service Workers
Who here knows what a Service Worker is?
Explain benefits of a service worker,
offline, preloading etc…
Extending A-Frame
Great guide to making your own components:
Component - A-Frame
_A web framework for building virtual reality experiences. Make WebVR with HTML and the Entity-Component ecosystem…_aframe.io
Tagged in Virtual Reality, JavaScript, A Frame
By Ada Rose Cannon on January 9, 2017.
